The Cybersecurity Capability Maturity Model (C2M2) is a free tool to help organizations evaluate their cybersecurity capabilities and optimize security investments. It uses a set of industry-vetted cybersecurity practices focused on both information technology (IT) and operations technology (OT) assets and environments.
While the U.S. energy industry led development of the C2M2 and championed its adoption, any organization—regardless of size, type, or industry—can use the model to evaluate, prioritize, and improve their cybersecurity capabilities.
Model Document
Self-Evaluation Tools
The tool, available on two platforms, offers interactive features and help text, allows users to securely record results, and automatically generates a detailed, graphical report. Results from either version can be saved and loaded into the other platform.
An organization can complete a self-evaluation using the C2M2 tools in as little as one day. If requested, DOE can also facilitate a free C2M2 self-evaluation for U.S. energy sector organizations. Email us at C2M2@hq.doe.gov for more information.
Download the C2M2 Version 2.1 – Latest version, released June 2022
HTML-based Self-Evaluation Tool: Access the tool at c2m2.doe.gov
PDF-based Self-Evaluation Tool: Send a request to C2M2@hq.doe.gov
In both tools, all user data remains only on user devices.
Additional Resources
| Self-Evaluation Guide | Guides users to plan and facilitate a self-evaluation workshop with key participants in their organization |
| Self-Evaluation Workshop Kickoff Presentation | Supports planning for a self-evaluation workshop |
| HTML-based Tool User Guide | Step-by-step guide to using the HTML-Based Self-Evaluation Tool |
| PDF-based Tool User Guide | Step-by-step guide to using the Self-Evaluation Tool |
| C2M2 Model Practices (Excel file) | Provides C2M2 practices and help text in a spreadsheet format |
| C2M2 Overview Presentation | Introduces C2M2 to key decision makers |
| Self-Evaluation Cheat Sheet | Offers a placemat-style reference guide for participants during a self-evaluation |
| C2M2 to CSF Mappings | Bi-directional mappings between the NIST Cybersecurity Framework V1.1 and the C2M2 (V2.1 and V2.0) practices, demonstrating strong alignment between the frameworks |
| C2M2 Legacy Mapping: V1.1 to V2.1 | Maps model practices in V1.1 to V2.1 to aid in updating self-evaluations |
| C2M2 Legacy Mapping: V2.0 to V2.1 | Maps model practices in V2.0 to V2.1 to aid in updating self-evaluations |
| C2M2-CMMC Supplemental Guidance | Supplemental guidance for C2M2 users subject to the Department of Defense Cybersecurity Maturity Model Certification (CMMC) |
| Sample Threat Profile (coming soon) | Offers an example of an organization’s threat profile, referenced by multiple C2M2 practices |
Read the Version 2.1 announcement to see what’s new in this version and how the model was updated.
What is a Maturity Model?
- A Crawl/Walk/Run-style set of characteristics, practices, or processes that represent the progression of capabilities in a particular discipline
- A tool to benchmark current capabilities and identify goals and priorities for improvement
Organizations can use the C2M2 to consistently measure their cybersecurity capabilities over time, identify target maturity levels based on risk, and prioritize the actions and investments that allow them to meet their targets.

C2M2 User Community
U.S. energy organizations have been using the C2M2 to evaluate and improve their cybersecurity capabilities for more than a decade. Since 2012, DOE has responded to more than 2,400 requests for the C2M2 PDF-based Tool from owners and operators in U.S. critical infrastructure sectors and international partners that are adopting the model. Increasing tool requests suggests a growing adoption of the C2M2 across the globe.
History of the C2M2
DOE developed the C2M2 in 2012 with energy and cybersecurity industry experts, in support of a White House initiative focused on assessing the security posture of the electricity industry. Hundreds of energy sector stakeholders have participated in subsequent model updates.
Version 1.1, released in 2014, included three versions targeting users in the electricity sector, oil and natural gas sector, and all sectors. Version 2.0, released July 2021, unified the model into one version tailored for the energy sector and made significant updates to reflect changing technology, threats, and security approaches. Version 2.1 – the latest release from June 2022 – made further refinements to the model and tools.
Components of the C2M2
The model contains more than 350 cybersecurity practices, which are grouped by objective into 10 logical domains. Each practice is assigned a maturity indicator level (MIL) that indicates the progression of practices within a domain.
Domains
A domain contains a structured set of cybersecurity practices focused on a specific subject area. For example, the Risk Management domain is a group of practices that an organization can perform to establish and mature its cyber risk management capability.

Objectives
Practices within each domain are organized into objectives that can be achieved by implementing the practices in the domain. For example, the Risk Management domain comprises five objectives:
- Establish and Maintain Cyber Risk Management Strategy and Program
- Identify Cyber Risk
- Analyze Cyber Risk
- Respond to Cyber Risk
- Management Activities
Practices
Practices are the most fundamental component of the C2M2. Each practice is a brief statement describing a cybersecurity activity that may be performed by an organization. Practices within each domain are organized to progress along a maturity scale.
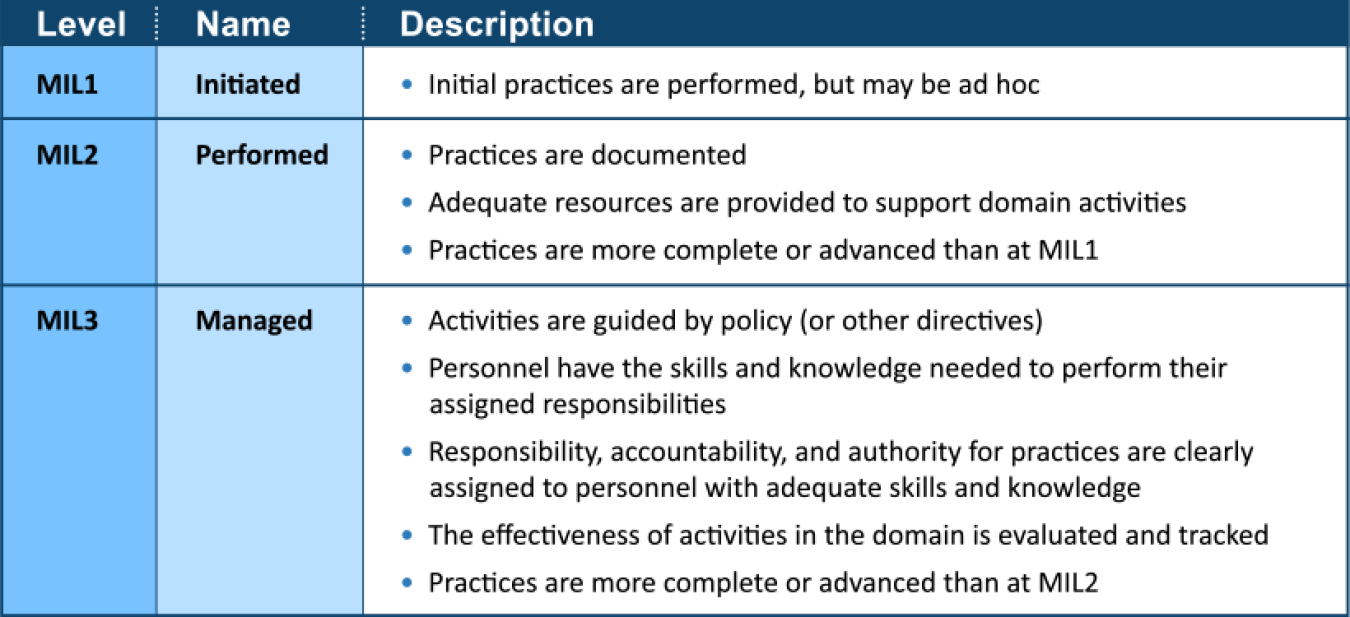
Maturity Indicator Levels (MILs)
To measure progression, the C2M2 uses a scale of maturity indicator levels, each representing maturity attributes described in the table below. Organizations that implement the cybersecurity practices within each MIL achieve that level.
Supplemental Materials
Energy Sector Cybersecurity Framework Implementation Guidance (PDF)
News and Updates
-
 The U.S. Department of Energy (DOE) Office of Cybersecurity, Energy Security, and Emergency Response (CESER) today released Version 2.1 (V2.1) of the Cybersecurity Capability Maturity Model (C2M2).
The U.S. Department of Energy (DOE) Office of Cybersecurity, Energy Security, and Emergency Response (CESER) today released Version 2.1 (V2.1) of the Cybersecurity Capability Maturity Model (C2M2). -
 The Department of Energy is seeking public comment on Version 2.0 of the Cybersecurity Capability Maturity Model (C2M2) through February 10, 2022.
The Department of Energy is seeking public comment on Version 2.0 of the Cybersecurity Capability Maturity Model (C2M2) through February 10, 2022. -
 U.S. energy companies have been using the Cybersecurity Capability Maturity Model (C2M2) to evaluate their cybersecurity capabilities and optimize their security investments for nearly a decade.
U.S. energy companies have been using the Cybersecurity Capability Maturity Model (C2M2) to evaluate their cybersecurity capabilities and optimize their security investments for nearly a decade. -
 The U.S. Department of Energy (DOE) today released Version 2.0 (V2.0) of the Cybersecurity Capability Maturity Model (C2M2)
The U.S. Department of Energy (DOE) today released Version 2.0 (V2.0) of the Cybersecurity Capability Maturity Model (C2M2)

