Scout is a tool for estimating the energy and carbon impacts of various energy conservation measures (ECMs) on the U.S. residential and commercial building sectors.

Scout characterizes ECMs using their relative or absolute performance, installed cost, service lifetime, and year of introduction into the market. Probability distributions can be placed on ECM performance, cost, and lifetime inputs, which then propagate through to final energy and carbon impacts. Furthermore, ECM energy performance can be calculated using whole-building energy simulation with EnergyPlus on prototype building models. This approach compares ECMs on a level playing field using identical assumptions, avoiding the need for normalization. It also produces savings estimates disaggregated by end use, which facilitates the evaluation of ECM packages.
Scout ECMs are applied to a baseline U.S. building stock that is defined from the Energy Information Administration’s (EIA) Annual Energy Outlook (AEO) at the granularity of building type (e.g., office, hospital, single family home), building vintage (e.g., new, existing), climate zone (e.g., hot and humid, cold), end use (e.g., heating, lighting), and fuel type (e.g., electricity, natural gas). Scout also uses AEO to project growth and stock turnover in each baseline market segment.
ECMs can currently be applied to the baseline buildings stock under two consumer adoption scenarios. In a technical potential adoption scenario, an ECM is assumed to fully capture its baseline market upon introduction and retain full market saturation in subsequent years. In a maximum adoption scenario, an ECM is only able to capture the segments of its baseline markets that are new and existing retrofit or replacement, considering realistic rates of new construction, retrofits, and turnover in baseline equipment.
Scout can also evaluate a portfolio of ECMs competitively, ensuring that ECM savings impacts are not double-counted. In such cases, multiple ECMs that apply to the same market segment compete for portions of this segment on the basis of cost effectiveness, which can be flexibly defined as simple payback, internal rate of return (IRR), cost of conserved energy (CCE), or cost of conserved carbon (CCC). In general, ECMs with lower incremental capital costs and higher operational cost savings across their lifetimes capture larger portions of competed market segments.
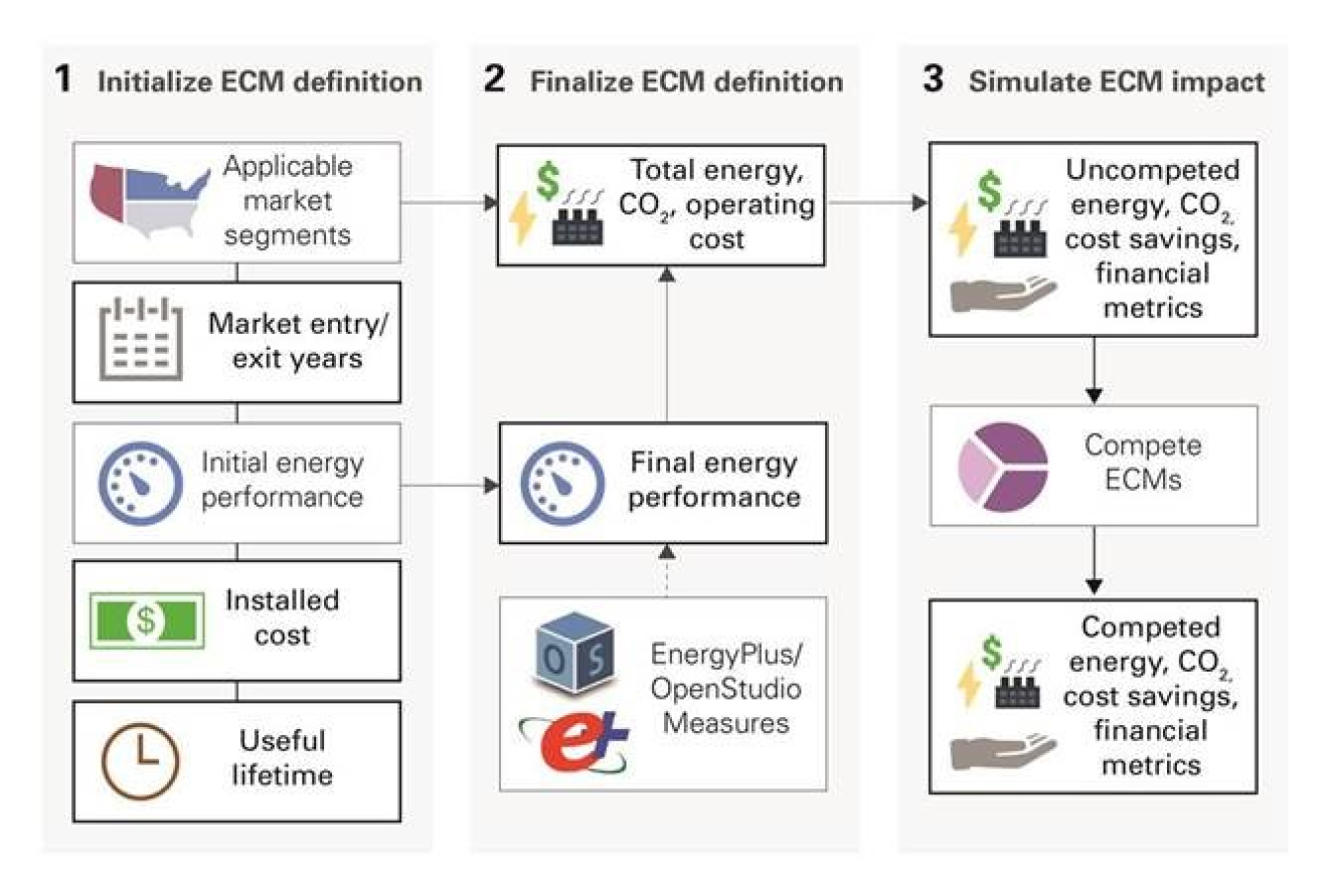
Scout ECM analyses require establishing an initial ECM definition; finalizing the ECM definition; simulating ECM energy, carbon, and cost impacts both with and without competition between the full portfolio of ECMs considered.
Applications
BTO primarily uses Scout to inform its technology R&D investment strategy. Specifically, it uses Scout to identify impactful technology areas, and to set performance, cost, lifetime, and market introduction targets for technologies in those areas to create a technology portfolio that can meet overall 2030 energy savings targets. Outputs from Scout are referenced by BTO in conjunction with stakeholder input and recommendations from technology road mapping exercises.
Scout is designed to be a flexible tool that can be adapted to the needs of users outside of BTO. For example, Scout baseline markets could be refined using scaling factors to model subsets of the U.S. building stock that represent a specific region, state, or city. Given this capability, utilities may be interested in using Scout to develop ECM incentives portfolios for their service territories. Researchers and educators may also wish to leverage Scout in exploring the national impact potential for new technologies of interest. The Scout software is free to use under an open-source license; get started here.
Development Status
Scout is currently under active development.
